Introductory HTML and JavaScript
Read: 01 submission
Hello, This is Fatima. You can view my Markdown webpage using the following link
You can go back to the home page.
In this blog I will give a summary for the chapters 1, 8, 17 and 18 of the book: “HTML & CSS” and chapter 1 from the book: “Javascript and Jquery” :books: :
- Chapter 1: Structure ✔️
- Chapter 8: Extra Markup ✔️
- Chapter 17: HTML5 Layout ✔️
- Chapter 18: Process & Design ✔️
- Chapter 1: The ABC of Programming ✔️
Note: Keywords are emphasised.
Chapter 1: Structure
- HTML pages are text documents.
- HTML uses tags (characters that sit inside angled brackets) to give the information they surround special meaning.
- Tags are often referred to as elements.
- Tags usually come in pairs.
- The opening tag denotes the start of a piece of content; the closing tag denotes the end.
- Opening tags can carry attributes, which tell us more about the content of that element.
- Attributes require a name and a value.
- To learn HTML you need to know what tags are available for you to use, and what they do.
This is an image shows the structure of the HTML page
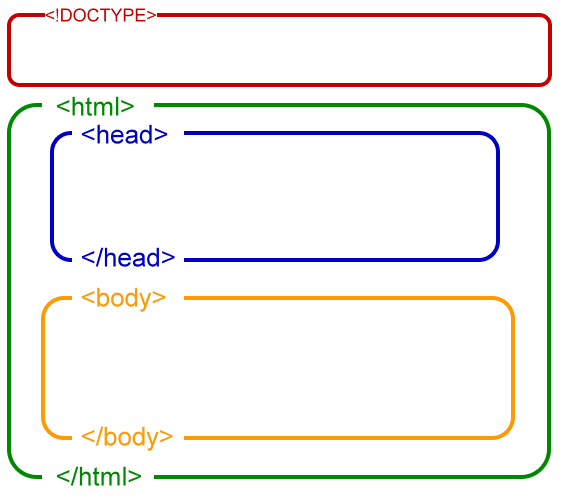
## Chapter 8: Extra Markup
- DOCTYPES tell browsers which version of HTML you are using.
- You can add comments to your code between the markers.
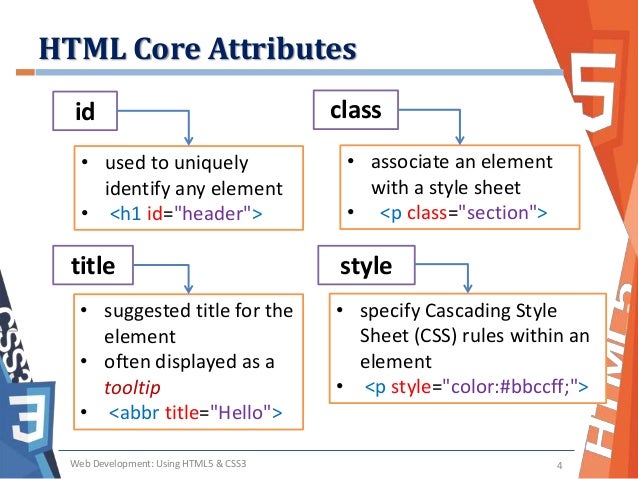
- The id and class attributes allow you to identify particular elements.
- The
<div>and<span>elements allow you to group block-level and inline elements together. <iframes>cut windows into your web pages through which other pages can be displayed.- The
<meta>tag allows you to supply all kinds of information about your web page. - Escape characters are used to include special characters in your pages such as
<,>, and©.
The two images below shows some markups:

Chapter 17: HTML5 Layout
- The new HTML5 elements indicate the purpose of different parts of a web page and help to describe its structure.
- The new elements provide clearer code (compared with using multiple <div> elements).
- Older browsers that do not understand HTML5 elements need to be told which elements are block-level elements.
- To make HTML5 elements work in Internet Explorer 8 (and older versions of IE), extra JavaScript is needed, which is available free from Google.
The image below shows a HTML layout structure

Chapter 18: Process & Design
- It’s important to understand who your target audience is, why they would come to your site, what information they want to find and when they are likely to return.
- Site maps allow you to plan the structure of a site.
- Wireframes allow you to organize the information that will need to go on each page.
- Design is about communication. Visual hierarchy helps visitors understand what you are trying to tell them.
- You can differentiate between pieces of information using size, color, and style.
- You can use grouping and similarity to help simplify the information you present.
The below images shows a HTML page design with the best practices
Chapter 1: The ABC of programming
- A script is a series of instructions that the computer can follow in order to achieve a goal.
- Each time the script runs, it might only use a subset of all the instructions.
- Computers approach tasks in a different way than humans, so yhe instructions must let the computer solve the task prggrammatically.
- To approach writing a script, break down the goal into a series of tasks and then work out each step needed to complete that task.
HTML dictionary

CSS cheat sheet

This is a table shows the difference between HTML, CSS and Javascript
| HTML | CSS | Javascript |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Presentation | Behavior |
| “What does it mean?” | “What does it look like” | “What does it do?” |